Nihonium
unsur kimia dengan lambang Nh dan nomor atom 113
Nihonium adalah unsur kimia sintetik dan transuranium dan transaktinida dalam sistem periodik unsur yang memiliki lambang Nh dan nomor atom 113.
113Nh Nihonium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
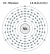
 Konfigurasi elektron nihonium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sifat umum | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pengucapan | /nihonium/ | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nihonium dalam tabel periodik | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nomor atom (Z) | 113 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Golongan | golongan 13 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Periode | periode 7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Blok | blok-p | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kategori unsur | tak diketahui, mungkin logam miskin | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nomor massa | [286] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Konfigurasi elektron | [Rn] 5f14 6d10 7s2 7p1 (diprediksi)[1] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Elektron per kelopak | 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 18, 3 (diprediksi) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sifat fisik | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fase pada STS (0 °C dan 101,325 kPa) | padat (prediksi)[1][2][3] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Titik lebur | 700 K (430 °C, 810 °F) (diprediksi)[1] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Titik didih | 1430 K (1130 °C, 2070 °F) (diprediksi)[1][4] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kepadatan mendekati s.k. | 16 g/cm3 (diprediksi)[4] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kalor peleburan | 7,61 kJ/mol (diekstrapolasi)[3] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kalor penguapan | 130 kJ/mol (diprediksi)[2][4] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sifat atom | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bilangan oksidasi | (−1), (+1), (+3), (+5) (diprediksi)[1][4][5] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Energi ionisasi | ke-1: 704,9 kJ/mol (diprediksi)[1] ke-2: 2240 kJ/mol (diprediksi)[4] ke-3: 3020 kJ/mol (diprediksi)[4] (artikel) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Jari-jari atom | empiris: 170 pm (diprediksi)[1] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Jari-jari kovalen | 172–180 pm (diekstrapolasi)[3] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lain-lain | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kelimpahan alami | sintetis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Struktur kristal | susunan padat heksagon (hcp) (diprediksi)[6][7] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nomor CAS | 54084-70-7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sejarah | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Penamaan | dari Jepang (Nihon dalam bahasa Jepang) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Penemuan | Riken (Jepang, klaim tak diperdebatkan pertama, 2004) JINR (Rusia) dan Livermore (AS, pengumuman pertama, 2003) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Isotop nihonium yang utama | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Nama
Nama "nihonium" berasal dari kata bahasa Jepang "Nihon" yang berarti Jepang/matahari. Nama kuno unsur ini adalah "ununtrium" (pengucapan: /juːˈnʌntriəm/ atau /əˈnʌntriəm/) dengan lambang "Uut" yang berarti "113".
Isotop
Senua isotop nihonium bersifat radioaktif, tidak ada isotop stabil. Isotop dengan waktu paruh yang terlama adalah nihonium-286, waktunya 10 sekon.
Referensi
- ^ a b c d e f g Hoffman, Darleane C.; Lee, Diana M.; Pershina, Valeria (2006). "Transactinides and the future elements". Dalam Morss; Edelstein, Norman M.; Fuger, Jean. The Chemistry of the Actinide and Transactinide Elements (edisi ke-3). Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Springer Science+Business Media. ISBN 978-1-4020-3555-5.
- ^ a b Seaborg, Glenn T. (sekitar 2006). "transuranium element (chemical element)". Encyclopædia Britannica. Diakses tanggal 7 Agustus 2022.
- ^ a b c Bonchev, Danail; Kamenska, Verginia (1981). "Predicting the Properties of the 113–120 Transactinide Elements". Journal of Physical Chemistry. American Chemical Society. 85 (9): 1177–1186. doi:10.1021/j150609a021.
- ^ a b c d e f Fricke, Burkhard (1975). "Superheavy elements: a prediction of their chemical and physical properties". Recent Impact of Physics on Inorganic Chemistry. Structure and Bonding. 21: 89–144. doi:10.1007/BFb0116498. ISBN 978-3-540-07109-9. Diakses tanggal 16 Juli 2022.
- ^ Thayer, John S. (2010). "Relativistic Effects and the Chemistry of the Heavier Main Group Elements". Dalam Barysz, Maria; Ishikawa, Yasuyuki. Relativistic Methods for Chemists. Challenges and Advances in Computational Chemistry and Physics. 10. Springer. hlm. 63–67. doi:10.1007/978-1-4020-9975-5_2. ISBN 978-1-4020-9974-8.
- ^ Keller, O. L., Jr.; Burnett, J. L.; Carlson, T. A.; Nestor, C. W., Jr. (1969). "Predicted Properties of the Super Heavy Elements. I. Elements 113 and 114, Eka-Thallium and Eka-Lead". The Journal of Physical Chemistry. 74 (5): 1127−1134. doi:10.1021/j100700a029.
- ^ Atarah, Samuel A.; Egblewogbe, Martin N. H.; Hagoss, Gebreyesus G. (2020). "First principle study of the structural and electronic properties of Nihonium". MRS Advances: 1–9. doi:10.1557/adv.2020.159.
- ^ Hofmann, S.; Heinz, S.; Mann, R.; Maurer, J.; Münzenberg, G.; Antalic, S.; Barth, W.; Burkhard, H. G.; Dahl, L.; Eberhardt, K.; Grzywacz, R.; Hamilton, J. H.; Henderson, R. A.; Kenneally, J. M.; Kindler, B.; Kojouharov, I.; Lang, R.; Lommel, B.; Miernik, K.; Miller, D.; Moody, K. J.; Morita, K.; Nishio, K.; Popeko, A. G.; Roberto, J. B.; Runke, J.; Rykaczewski, K. P.; Saro, S.; Schneidenberger, C.; Schött, H. J.; Shaughnessy, D. A.; Stoyer, M. A.; Thörle-Pospiech, P.; Tinschert, K.; Trautmann, N.; Uusitalo, J.; Yeremin, A. V. (2016). "Remarks on the Fission Barriers of SHN and Search for Element 120". Dalam Peninozhkevich, Yu. E.; Sobolev, Yu. G. Exotic Nuclei: EXON-2016 Proceedings of the International Symposium on Exotic Nuclei. Exotic Nuclei. hlm. 155–164. ISBN 9789813226555.
- ^ Hofmann, S.; Heinz, S.; Mann, R.; Maurer, J.; Münzenberg, G.; Antalic, S.; Barth, W.; Burkhard, H. G.; Dahl, L.; Eberhardt, K.; Grzywacz, R.; Hamilton, J. H.; Henderson, R. A.; Kenneally, J. M.; Kindler, B.; Kojouharov, I.; Lang, R.; Lommel, B.; Miernik, K.; Miller, D.; Moody, K. J.; Morita, K.; Nishio, K.; Popeko, A. G.; Roberto, J. B.; Runke, J.; Rykaczewski, K. P.; Saro, S.; Scheidenberger, C.; Schött, H. J.; Shaughnessy, D. A.; Stoyer, M. A.; Thörle-Popiesch, P.; Tinschert, K.; Trautmann, N.; Uusitalo, J.; Yeremin, A. V. (2016). "Review of even element super-heavy nuclei and search for element 120". The European Physics Journal A. 2016 (52). Bibcode:2016EPJA...52..180H. doi:10.1140/epja/i2016-16180-4.
Pranala luar
Wikimedia Commons memiliki media mengenai Nihonium.