Nihonium
unsur kimia dengan lambang Nh dan nomor atom 113
Ununtrium {pengucapan: /juːˈnʌntriəm/ atau /əˈnʌntriəm/) adalah unsur kimia sintetik dalam sistem periodik unsur yang memiliki lambang Uut dan nomor atom 113.
113Nh Nihonium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
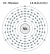
 Konfigurasi elektron nihonium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sifat umum | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pengucapan | /nihonium/ | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nihonium dalam tabel periodik | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nomor atom (Z) | 113 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Golongan | golongan 13 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Periode | periode 7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Blok | blok-p | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kategori unsur | tak diketahui, mungkin logam miskin | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nomor massa | [286] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Konfigurasi elektron | [Rn] 5f14 6d10 7s2 7p1 (diprediksi)[1] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Elektron per kelopak | 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 18, 3 (diprediksi) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sifat fisik | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fase pada STS (0 °C dan 101,325 kPa) | padat (prediksi)[1][2][3] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Titik lebur | 700 K (430 °C, 810 °F) (diprediksi)[1] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Titik didih | 1430 K (1130 °C, 2070 °F) (diprediksi)[1][4] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kepadatan mendekati s.k. | 16 g/cm3 (diprediksi)[4] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kalor peleburan | 7,61 kJ/mol (diekstrapolasi)[3] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kalor penguapan | 130 kJ/mol (diprediksi)[2][4] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sifat atom | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bilangan oksidasi | (−1), (+1), (+3), (+5) (diprediksi)[1][4][5] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Energi ionisasi | ke-1: 704,9 kJ/mol (diprediksi)[1] ke-2: 2240 kJ/mol (diprediksi)[4] ke-3: 3020 kJ/mol (diprediksi)[4] (artikel) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Jari-jari atom | empiris: 170 pm (diprediksi)[1] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Jari-jari kovalen | 172–180 pm (diekstrapolasi)[3] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lain-lain | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kelimpahan alami | sintetis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Struktur kristal | susunan padat heksagon (hcp) (diprediksi)[6][7] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nomor CAS | 54084-70-7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sejarah | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Penamaan | dari Jepang (Nihon dalam bahasa Jepang) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Penemuan | Riken (Jepang, klaim tak diperdebatkan pertama, 2004) JINR (Rusia) dan Livermore (AS, pengumuman pertama, 2003) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Isotop nihonium yang utama | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Referensi
- ^ a b c d e f g Hoffman, Darleane C.; Lee, Diana M.; Pershina, Valeria (2006). "Transactinides and the future elements". Dalam Morss; Edelstein, Norman M.; Fuger, Jean. The Chemistry of the Actinide and Transactinide Elements (edisi ke-3). Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Springer Science+Business Media. ISBN 978-1-4020-3555-5.
- ^ a b Seaborg, Glenn T. (sekitar 2006). "transuranium element (chemical element)". Encyclopædia Britannica. Diakses tanggal 7 Agustus 2022.
- ^ a b c Bonchev, Danail; Kamenska, Verginia (1981). "Predicting the Properties of the 113–120 Transactinide Elements". Journal of Physical Chemistry. American Chemical Society. 85 (9): 1177–1186. doi:10.1021/j150609a021.
- ^ a b c d e f Fricke, Burkhard (1975). "Superheavy elements: a prediction of their chemical and physical properties". Recent Impact of Physics on Inorganic Chemistry. Structure and Bonding. 21: 89–144. doi:10.1007/BFb0116498. ISBN 978-3-540-07109-9. Diakses tanggal 16 Juli 2022.
- ^ Thayer, John S. (2010). "Relativistic Effects and the Chemistry of the Heavier Main Group Elements". Dalam Barysz, Maria; Ishikawa, Yasuyuki. Relativistic Methods for Chemists. Challenges and Advances in Computational Chemistry and Physics. 10. Springer. hlm. 63–67. doi:10.1007/978-1-4020-9975-5_2. ISBN 978-1-4020-9974-8.
- ^ Keller, O. L., Jr.; Burnett, J. L.; Carlson, T. A.; Nestor, C. W., Jr. (1969). "Predicted Properties of the Super Heavy Elements. I. Elements 113 and 114, Eka-Thallium and Eka-Lead". The Journal of Physical Chemistry. 74 (5): 1127−1134. doi:10.1021/j100700a029.
- ^ Atarah, Samuel A.; Egblewogbe, Martin N. H.; Hagoss, Gebreyesus G. (2020). "First principle study of the structural and electronic properties of Nihonium". MRS Advances: 1–9. doi:10.1557/adv.2020.159.
- ^ Hofmann, S.; Heinz, S.; Mann, R.; Maurer, J.; Münzenberg, G.; Antalic, S.; Barth, W.; Burkhard, H. G.; Dahl, L.; Eberhardt, K.; Grzywacz, R.; Hamilton, J. H.; Henderson, R. A.; Kenneally, J. M.; Kindler, B.; Kojouharov, I.; Lang, R.; Lommel, B.; Miernik, K.; Miller, D.; Moody, K. J.; Morita, K.; Nishio, K.; Popeko, A. G.; Roberto, J. B.; Runke, J.; Rykaczewski, K. P.; Saro, S.; Schneidenberger, C.; Schött, H. J.; Shaughnessy, D. A.; Stoyer, M. A.; Thörle-Pospiech, P.; Tinschert, K.; Trautmann, N.; Uusitalo, J.; Yeremin, A. V. (2016). "Remarks on the Fission Barriers of SHN and Search for Element 120". Dalam Peninozhkevich, Yu. E.; Sobolev, Yu. G. Exotic Nuclei: EXON-2016 Proceedings of the International Symposium on Exotic Nuclei. Exotic Nuclei. hlm. 155–164. ISBN 9789813226555.
- ^ Hofmann, S.; Heinz, S.; Mann, R.; Maurer, J.; Münzenberg, G.; Antalic, S.; Barth, W.; Burkhard, H. G.; Dahl, L.; Eberhardt, K.; Grzywacz, R.; Hamilton, J. H.; Henderson, R. A.; Kenneally, J. M.; Kindler, B.; Kojouharov, I.; Lang, R.; Lommel, B.; Miernik, K.; Miller, D.; Moody, K. J.; Morita, K.; Nishio, K.; Popeko, A. G.; Roberto, J. B.; Runke, J.; Rykaczewski, K. P.; Saro, S.; Scheidenberger, C.; Schött, H. J.; Shaughnessy, D. A.; Stoyer, M. A.; Thörle-Popiesch, P.; Tinschert, K.; Trautmann, N.; Uusitalo, J.; Yeremin, A. V. (2016). "Review of even element super-heavy nuclei and search for element 120". The European Physics Journal A. 2016 (52). Bibcode:2016EPJA...52..180H. doi:10.1140/epja/i2016-16180-4.
Pranala luar
Wikimedia Commons memiliki media mengenai Ununtrium.
- WebElements.com - Uut
- Uut and Uup Add Their Atomic Mass to Periodic Table
- Apsidium - Ununtrium
- Discovery of Elements 113 and 115
- Superheavy elements