Europium
unsur kimia dengan lambang Eu dan nomor atom 63
Europium adalah suatu unsur kimia dalam tabel periodik yang memiliki lambang Eu dan nomor atom 63.
63Eu Europium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Europium yang sedikit teroksidasi, berukuran 6×16 mm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Garis spektrum europium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sifat umum | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pengucapan |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Penampilan | putih keperakan, dengan warna kuning pucat;[2] tetapi jarang terlihat tanpa perubahan warna oksida | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
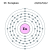
| Europium dalam tabel periodik | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nomor atom (Z) | 63 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Golongan | golongan n/a | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Periode | periode 6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Blok | blok-f | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kategori unsur | lantanida | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Berat atom standar (Ar) |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Konfigurasi elektron | [Xe] 4f7 6s2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Elektron per kelopak | 2, 8, 18, 25, 8, 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sifat fisik | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fase pada STS (0 °C dan 101,325 kPa) | padat | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Titik lebur | 1099 K (826 °C, 1519 °F) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Titik didih | 1802 K (1529 °C, 2784 °F) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kepadatan mendekati s.k. | 5,264 g/cm3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| saat cair, pada t.l. | 5,13 g/cm3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kalor peleburan | 9,21 kJ/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kalor penguapan | 176 kJ/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kapasitas kalor molar | 27,66 J/(mol·K) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Tekanan uap
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sifat atom | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bilangan oksidasi | 0,[3] +2, +3 (oksida agak basa) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Elektronegativitas | Skala Pauling: 1,2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Energi ionisasi | ke-1: 547,1 kJ/mol ke-2: 1085 kJ/mol ke-3: 2404 kJ/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Jari-jari atom | empiris: 180 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Jari-jari kovalen | 198±6 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lain-lain | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kelimpahan alami | primordial | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Struktur kristal | kubus berpusat badan (bcc) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ekspansi kalor | poli: 35,0 µm/(m·K) (pada s.k.) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Konduktivitas termal | est. 13,9 W/(m·K) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Resistivitas listrik | poli: 0,900 µΩ·m (pada s.k.) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Arah magnet | paramagnetik[4] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Suseptibilitas magnetik molar | +34.000,0×10−6 cm3/mol[5] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Modulus Young | 18,2 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Modulus Shear | 7,9 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Modulus curah | 8,3 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rasio Poisson | 0,152 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Skala Vickers | 165–200 MPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nomor CAS | 7440-53-1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sejarah | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Penamaan | dari Eropa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Penemuan dan isolasi pertama | E. Demarçay (1896, 1901) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Isotop europium yang utama | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Galeri
- Europium
Referensi
- ^ (Indonesia) "Europium". KBBI Daring. Diakses tanggal 17 Juli 2022.
- ^ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, A. (1997), Chemistry of the Elements (edisi ke-2), Oxford: Butterworth-Heinemann, hlm. 112, ISBN 0-7506-3365-4
- ^ Yttrium and all lanthanides except Ce and Pm have been observed in the oxidation state 0 in bis(1,3,5-tri-t-butylbenzene) complexes, see Cloke, F. Geoffrey N. (1993). "Zero Oxidation State Compounds of Scandium, Yttrium, and the Lanthanides". Chem. Soc. Rev. 22: 17–24. doi:10.1039/CS9932200017. and Arnold, Polly L.; Petrukhina, Marina A.; Bochenkov, Vladimir E.; Shabatina, Tatyana I.; Zagorskii, Vyacheslav V.; Cloke (2003-12-15). "Arene complexation of Sm, Eu, Tm and Yb atoms: a variable temperature spectroscopic investigation". Journal of Organometallic Chemistry. 688 (1–2): 49–55. doi:10.1016/j.jorganchem.2003.08.028.
- ^ Lide, D. R., ed. (2005). "Magnetic susceptibility of the elements and inorganic compounds". CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (PDF) (edisi ke-86). Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press. ISBN 0-8493-0486-5.
- ^ Weast, Robert (1984). CRC, Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. Boca Raton, Florida: Chemical Rubber Company Publishing. hlm. E110. ISBN 0-8493-0464-4.