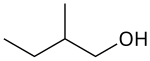
2-Metil-1-butanol
2-Metil-1-butanol (nama IUPAC, juga disebut amil alkohol aktif) adalah sebuah senyawa organik dengan rumus CH3CH2CH(CH3)CH2OH. Senyawa ini adalah salah satu dari beberapa isomer amil alkohol. Cairan nirwarna ini terjadi secara alami dalam jumlah kecil dan telah menarik perhatian sebagai bahan bakar hayati yang potensial, dengan memanfaatkan sifat hidrofobik (seperti bensin) dan struktur bercabangnya. Ia adalah molekul kiral.[3]
| |
| Nama | |
|---|---|
| Nama IUPAC (preferensi)
2-Metilbutan-1-ol | |
| Nama lain
2-Metil-1-butanol
Amil alkohol aktif | |
| Penanda | |
Model 3D (JSmol)
|
|
| 3DMet | {{{3DMet}}} |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| Nomor EC | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| Nomor RTECS | {{{value}}} |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Sifat | |
| C5H12O | |
| Massa molar | 88,148 g/mol |
| Penampilan | Cairan nirwarna |
| Densitas | 0,8152 g/cm3 |
| Titik lebur | −117,2 °C (−179,0 °F; 156,0 K) |
| Titik didih | 127,5 °C (261,5 °F; 400,6 K) |
| 31 g/L | |
| Kelarutan | pelarut organik |
| Tekanan uap | 3 mm Hg |
| Viskositas | 4,453 mPa·s |
| Termokimia | |
| Entalpi pembentukan standar (ΔfH |
−356,6 kJ·mol−1 (cairan) −301,4 kJ·mol−1 (gas) |
| Bahaya | |
| 385 °C (725 °F; 658 K) | |
| Senyawa terkait | |
Senyawa terkait
|
Amil alkohol |
Kecuali dinyatakan lain, data di atas berlaku pada suhu dan tekanan standar (25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Referensi | |
Kemunculan
sunting2-Metil-1-butanol adalah komponen dari banyak campuran amil alkohol komersial. Senyawa ini adalah salah satu dari banyak komponen aroma berbagai jamur dan buah, misalnya truffle musim panas, tomat,[4] dan blewah.[5][6]
Produksi dan reaksi
sunting2-Metil-1-butanol telah diproduksi dari glukosa oleh E. coli yang dimodifikasi secara genetik. 2-Keto-3-metilvalerat, prekursor treonina, diubah menjadi alkohol target melalui aksi berurutan dari asam 2-keto, dekarboksilase dan dehidrogenase.[7] Ia dapat berasal dari minyak fusel (karena terjadi secara alami pada buah-buahan seperti anggur[8]) atau diproduksi melalui proses okso atau halogenasi pentana.[2]
Lihat pula
suntingReferensi
sunting- ^ Lide, David R. (1998), Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (edisi ke-87), Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press, hlm. 3–374, 5–42, 6–188, 8–102, 16–22, ISBN 0-8493-0594-2
- ^ a b McKetta, John J.; Cunningham, William Aaron (1977), Encyclopedia of Chemical Processing and Design, 3, Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press, hlm. 279–280, ISBN 978-0-8247-2480-1, diakses tanggal 25 Januari 2024
- ^ Xiong, Ren-Gen; You, Xiao-Zeng; Abrahams, Brendan F.; Xue, Ziling; Che, Chi-Ming (2001). "Enantioseparation of Racemic Organic Molecules by a Zeolite Analogue". Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 40 (23): 4422–4425. doi:10.1002/1521-3773(20011203)40:23<4422::AID-ANIE4422>3.0.CO;2-G. PMID 12404434.
- ^ Buttery, Ron G.; Teranishi, Roy; Ling, Louisa C. (1987). "Fresh tomato aroma volatiles: A quantitative study". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 35 (4): 540–544. doi:10.1021/jf00076a025.
- ^ Dı́Az, P.; Ibáñez, E.; Señoráns, F.J; Reglero, G. (2003). "Truffle Aroma Characterization by Headspace solid-phase microextraction". Journal of Chromatography A. 1017 (1–2): 207–214. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2003.08.016. PMID 14584705.
- ^ Beaulieu, John C.; Grimm, Casey C. (2001). "Identification of Volatile Compounds in Cantaloupe at Various Developmental Stages Using Solid Phase Microextraction". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 49 (3): 1345–1352. doi:10.1021/jf0005768. PMID 11312862.
- ^ Atsumi, Shota; Hanai, Taizo; Liao, James C. (2008). "Non-Fermentative Pathways for Synthesis of Branched-Chain Higher Alcohols as Biofuels". Nature. 451 (7174): 86–89. Bibcode:2008Natur.451...86A. doi:10.1038/nature06450. PMID 18172501.
- ^ Howard, Philip H. (1993), Handbook of Environmental Fate and Exposure Data for Organic Chemicals, 4, Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press, hlm. 392–396, ISBN 978-0-87371-413-6, diakses tanggal 25 Januari 2024